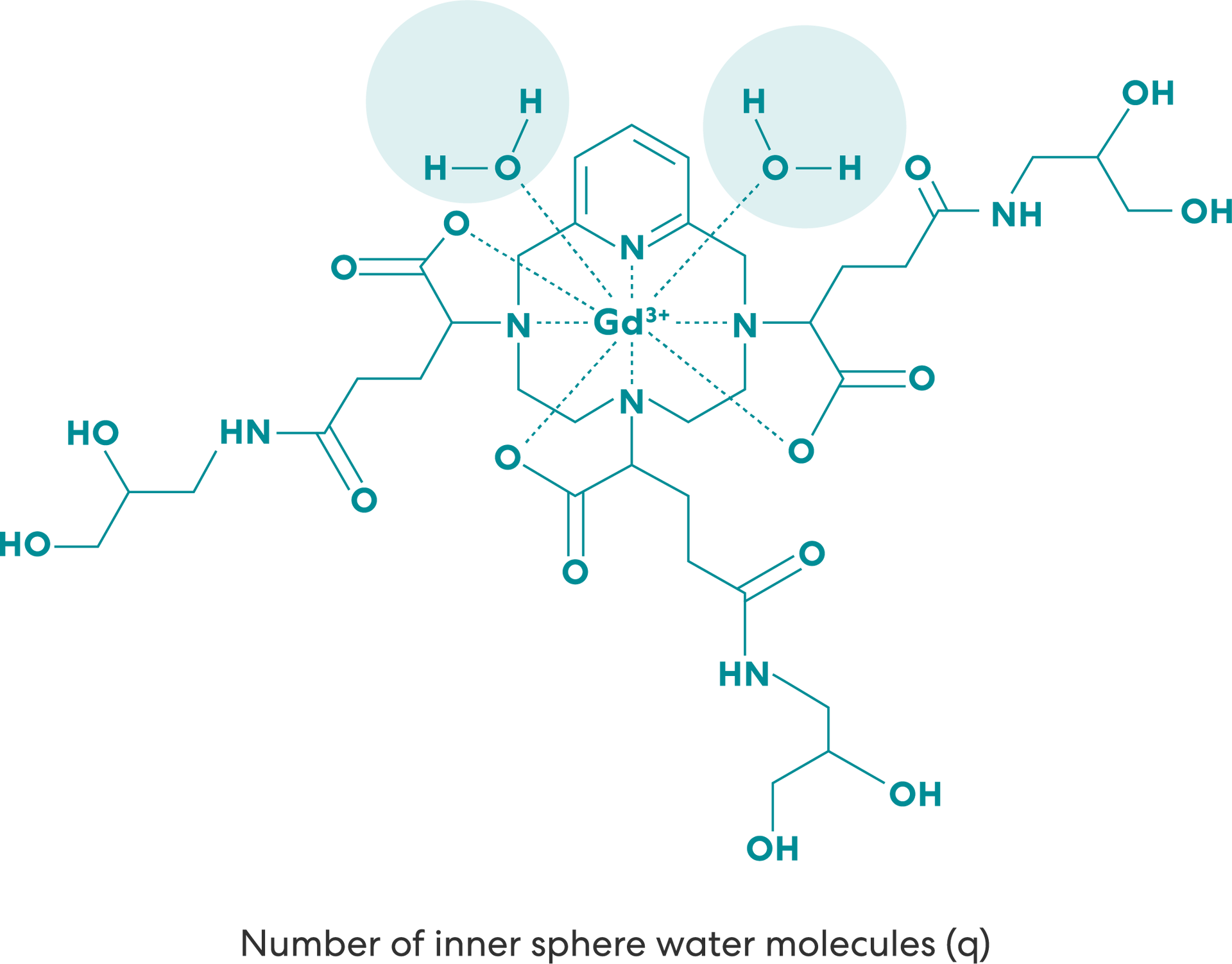
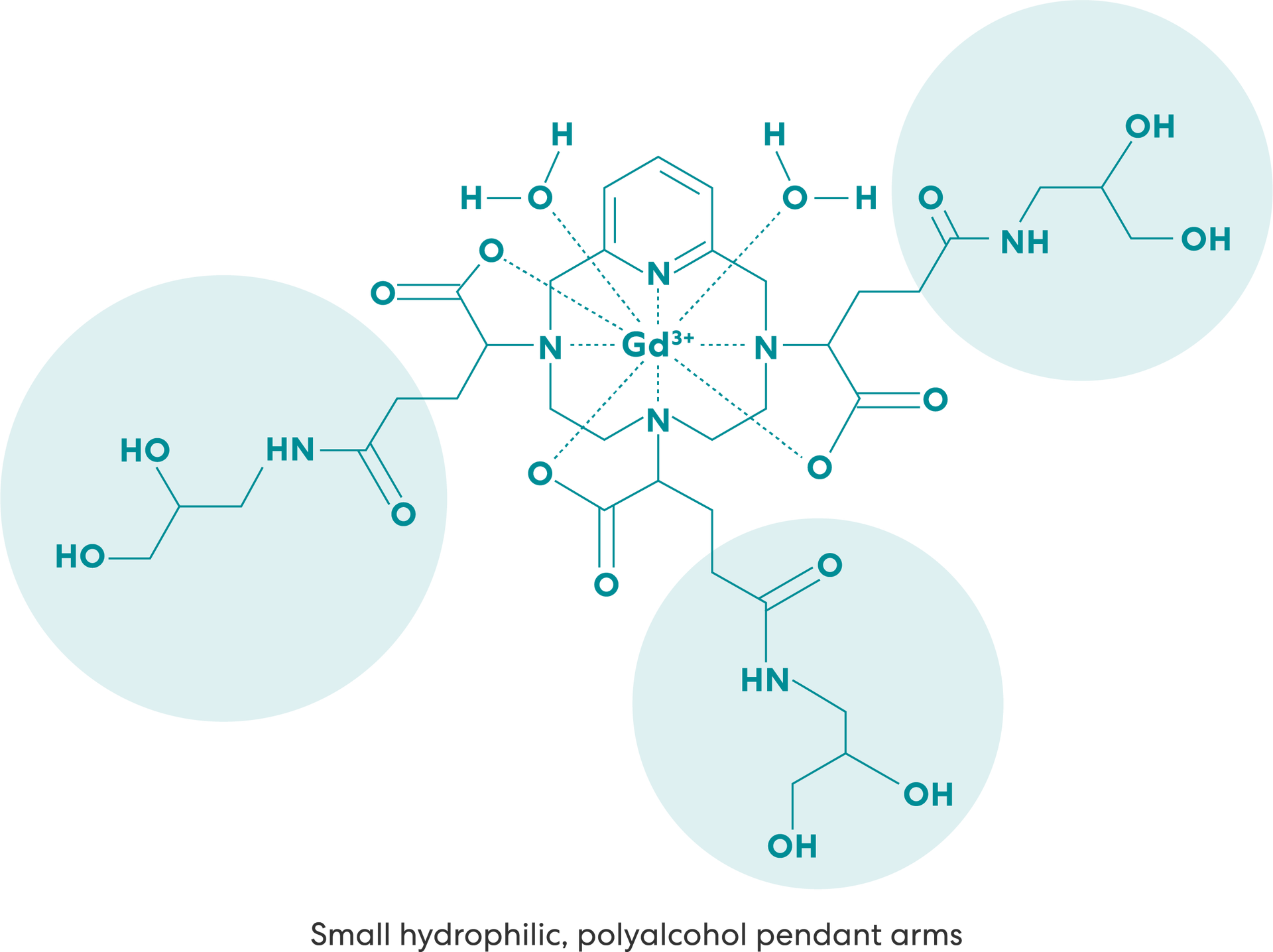
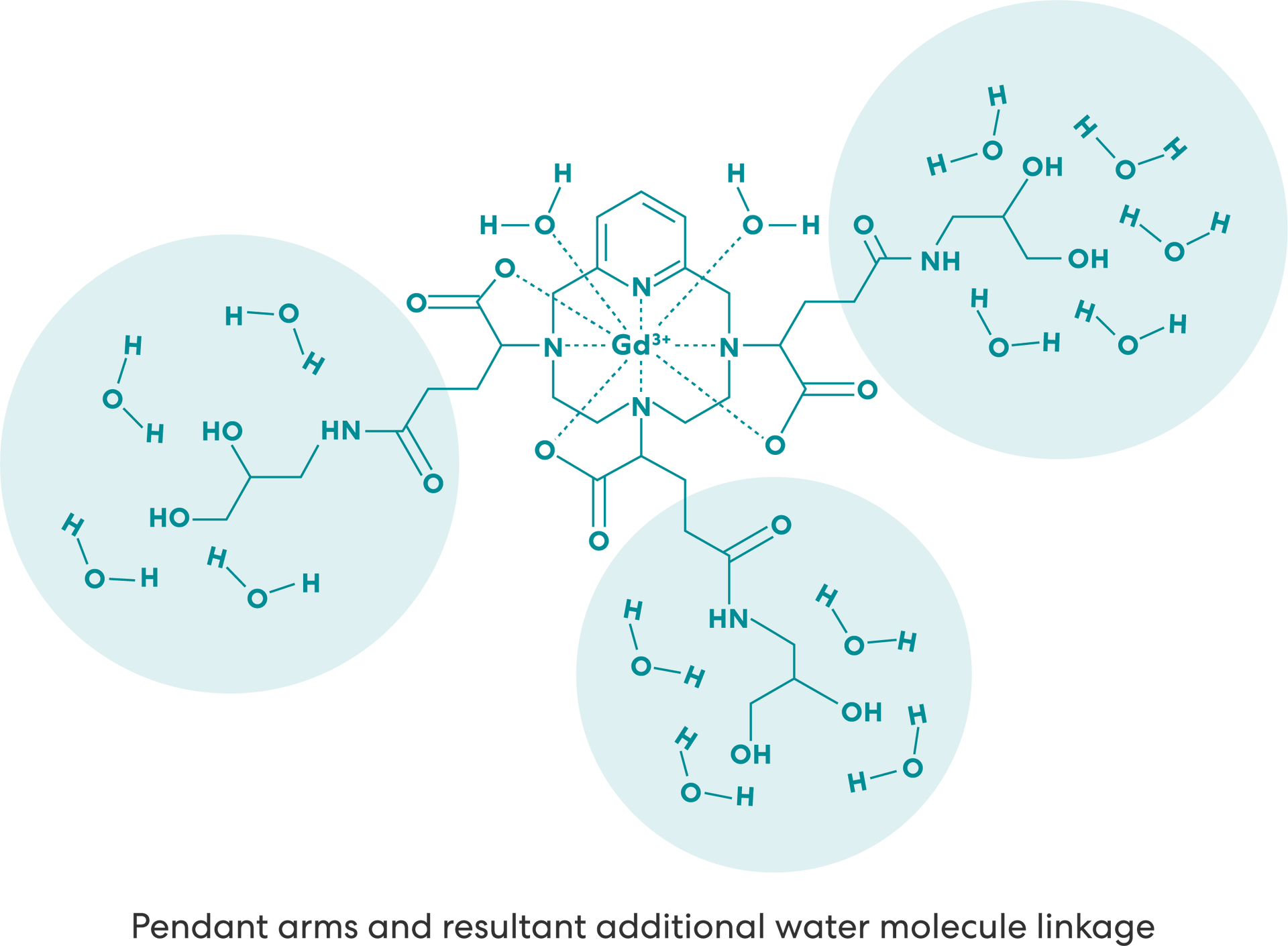
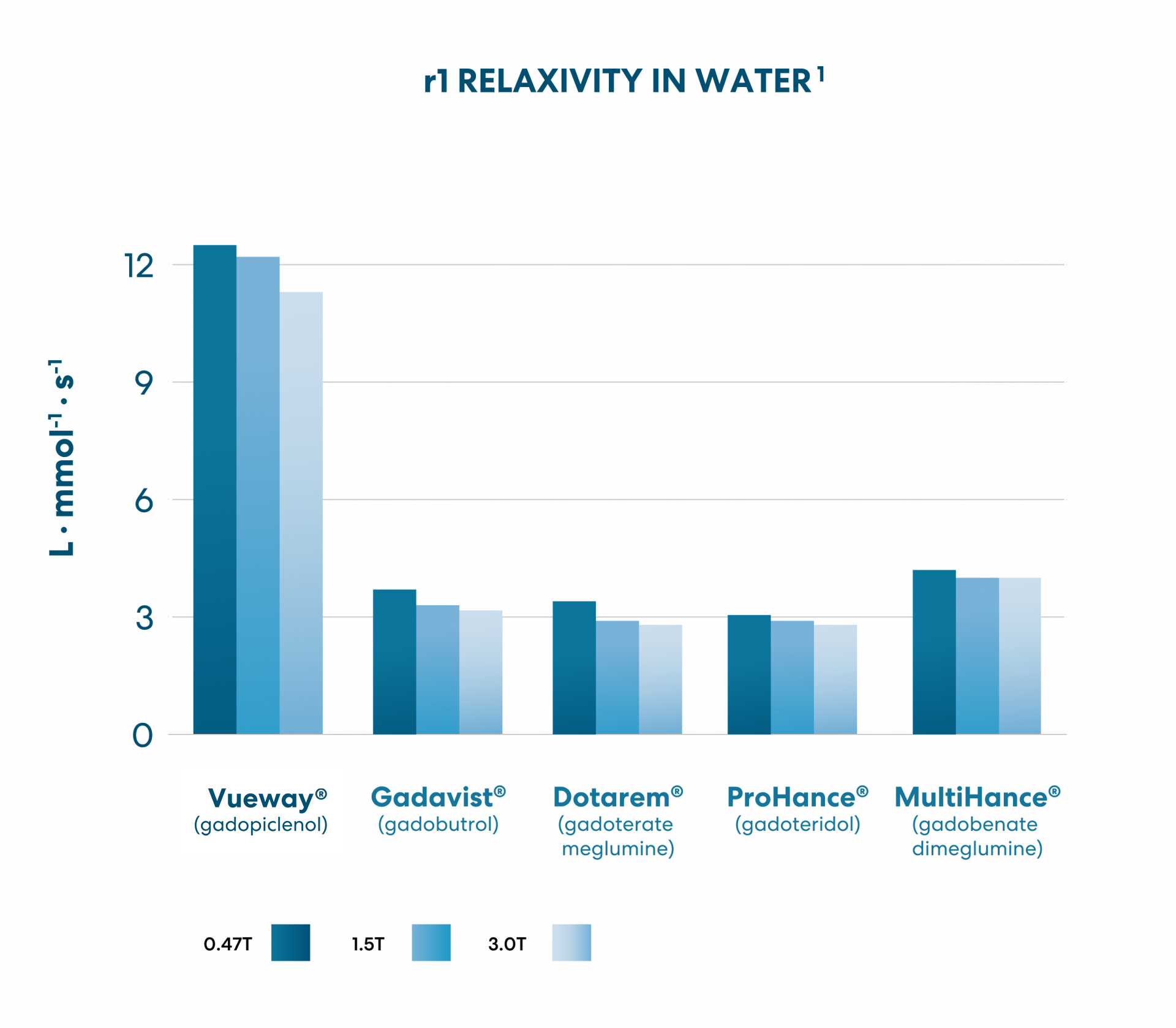
VUEWAY® (gadopiclenol) solution for injection
Indications
VUEWAY injection is indicated in adults and children aged 2 years and older for use with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to detect and visualize lesions with abnormal vascularity in:
• the central nervous system (brain, spine and surrounding tissues),
• the body (head and neck, thorax, abdomen, pelvis, and musculoskeletal system).
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
WARNING: RISK ASSOCIATED WITH INTRATHECAL USE and NEPHROGENIC SYSTEMIC FIBROSIS
Risk Associated with Intrathecal Use
Intrathecal administration of gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) can cause serious adverse reactions including death, coma, encephalopathy, and seizures. VUEWAY is not approved for intrathecal use.
NEPHROGENIC SYSTEMIC FIBROSIS
Gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) increase the risk for NSF among patients with impaired elimination of the drugs. Avoid use of GBCAs in these patients unless the diagnostic information is essential and not available with non-contrasted MRI or other modalities. NSF may result in fatal or debilitating fibrosis affecting the skin, muscle and internal organs.
- The risk for NSF appears highest among patients with:
- Chronic, severe kidney disease (GFR < 30 mL/min/1.73 m2), or
- Acute kidney injury.
- Screen patients for acute kidney injury and other conditions that may reduce renal function. For patients at risk for chronically reduced renal function (e.g. age > 60 years, hypertension, diabetes), estimate the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) through laboratory testing.
- For patients at highest risk for NSF, do not exceed the recommended VUEWAY dose and allow a sufficient period of time for elimination of the drug from the body prior to any re-administration.
Contraindications
VUEWAY injection is contraindicated in patients with history of hypersensitivity reactions to VUEWAY.
Warnings and Precautions
There are risks associated with intrathecal use of GBCAs that can cause serious adverse reactions including death, coma, encephalopathy, and seizures. The safety and effectiveness of VUEWAY have not been established with intrathecal use and VUEWAY is not approved for intrathecal use.
Risk of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis is increased in patients using GBCA agents that have impaired elimination of the drugs, with the highest risk in patients with chronic, severe kidney disease as well as patients with acute kidney injury. Avoid use of GBCAs among these patients unless the diagnostic information is essential and not available with non-contrast MRI or other modalities.
Hypersensitivity reactions, including serious hypersensitivity reactions, could occur during use or shortly following VUEWAY administration. Assess all patients for any history of a reaction to contrast media, bronchial asthma and/or allergic disorders, administer VUEWAY only in situations where trained personnel and therapies are promptly available for the treatment of hypersensitivity reactions, and observe patients for signs and symptoms of hypersensitivity reactions after administration.
Gadolinium retention can be for months or years in several organs after administration. The highest concentrations (nanomoles per gram of tissue) have been identified in the bone, followed by other organs (brain, skin, kidney, liver and spleen). Minimize repetitive GBCA imaging studies, particularly closely spaced studies, when possible.
Acute kidney injury requiring dialysis has occurred with the use of GBCAs in patients with chronically reduced renal function. The risk of acute kidney injury may increase with increasing dose of the contrast agent.
Extravasation and injection site reactions can occur with administration of VUEWAY. Ensure catheter and venous patency before the injection of VUEWAY.
VUEWAY may impair the visualization of lesions seen on non-contrast MRI. Therefore, caution should be exercised when VUEWAY MRI scans are interpreted without a companion non-contrast MRI scan.
The most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥ 0.5%) are injection site pain (0.7%), and headache (0.7%).
You are encouraged to report negative side effects of prescription drugs to the FDA. Visit www.fda.gov/medwatch or call 1-800-FDA-1088.
Please click here for full Prescribing Information for VUEWAY (gadopiclenol) solution for injection including BOXED WARNING on Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis.
Manufactured for Bracco Diagnostics Inc. by Liebel-Flarsheim Company LLC - Raleigh, NC, USA 27616.
VUEWAY is a registered trademark of Bracco Imaging S.p.A.
All other trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
COMBINED INDICATIONS and Important Safety Information for:
MultiHance® (gadobenate dimeglumine) injection, 529 mg/mL
and
ProHance® (Gadoteridol) Injection, 279.3 mg/mL
Indications and Usage for MultiHance® (gadobenate dimeglumine) injection, 529 mg/mL:
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the central nervous system (CNS) in adults and pediatric patients (including term neonates) to visualize lesions with abnormal blood-brain barrier or abnormal vascularity of the brain, spine, and associated tissues
- Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) to evaluate adults with known or suspected renal or aorto-ilio-femoral occlusive vascular disease
Indications and Usage for ProHance® (Gadoteridol) Injection, 279.3 mg/mL:
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
ProHance is indicated for use in MRI in adults and pediatric patients including term neonates to visualize lesions with disrupted blood-brain barrier and/or abnormal vascularity in the brain (intracranial lesions), spine, and associated tissues.
EXTRACRANIAL/EXTRASPINAL TISSUES
ProHance is indicated for use in MRI in adults to visualize lesions in the head and neck.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION for MultiHance and ProHance:
WARNING: RISK ASSOCIATED WITH INTRATHECAL USE and NEPHROGENIC SYSTEMIC FIBROSIS
Risk Associated with Intrathecal Use
Intrathecal administration of gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) can cause serious adverse reactions including death, coma, encephalopathy, and seizures. MultiHance and ProHance are not approved for intrathecal use.
NEPHROGENIC SYSTEMIC FIBROSIS
Gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) increase the risk for NSF among patients with impaired elimination of the drugs. Avoid use of GBCAs in these patients unless the diagnostic information is essential and not available with non-contrasted MRI or other modalities. NSF may result in fatal or debilitating systemic fibrosis affecting the skin, muscle and internal organs.
- The risk for NSF appears highest among patients with:
- chronic, severe kidney disease (GFR < 30 mL/min/1.73m2), or
- acute kidney injury.
- Screen patients for acute kidney injury and other conditions that may reduce renal function. For patients at risk for chronically reduced renal function (e.g. age > 60 years, hypertension or diabetes), estimate the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) through laboratory testing.
- For patients at highest risk for NSF, do not exceed the recommended MultiHance and ProHance dose and allow a sufficient period of time for elimination of the drug from the body prior to re-administration.
MultiHance (gadobenate dimeglumine) injection, 529 mg/mL
CONTRAINDICATIONS
MultiHance is contraindicated in patients with known allergic or hypersensitivity reactions to gadolinium-based contrast agents.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Risk Associated with Intrathecal Use: Intrathecal administration of GBCAs can cause serious adverse reactions including death, coma, encephalopathy, and seizures. The safety and effectiveness of MultiHance have not been established with intrathecal use and MultiHance is not approved for intrathecal use.
Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis: NSF has occurred in patients with impaired elimination of GBCAs. Higher than recommended dosing or repeated dosing appears to increase risk.
Hypersensitivity Reactions: Anaphylactic and anaphylactoid reactions have been reported, involving cardiovascular, respiratory, and/or cutaneous manifestations. Some patients experienced circulatory collapse and died. In most cases, initial symptoms occurred within minutes of MultiHance administration and resolved with prompt emergency treatment. Consider the risk for hypersensitivity reactions, especially in patients with a history of hypersensitivity reactions or a history of asthma or other allergic disorders.
Gadolinium Retention: Gadolinium is retained for months or years in several organs. The highest concentrations have been identified in the bone, followed by brain, skin, kidney, liver, and spleen. At equivalent doses, retention varies among the linear agents. Retention is lowest and similar among the macrocyclic GBCAs. Consequences of gadolinium retention in the brain have not been established, but they have been established in the skin and other organs in patients with impaired renal function. Minimize repetitive GBCA imaging studies, particularly closely spaced studies when possible.
Acute Renal Failure: In patients with renal insufficiency, acute renal failure requiring dialysis or worsening renal function have occurred with the use of GBCAs. The risk of renal failure may increase with increasing dose of the contrast agent. Screen all patients for renal dysfunction by obtaining a history and/or laboratory tests.
Extravasation and Injection Site Reactions: Extravasation of MultiHance may lead to injection site reactions, characterized by local pain or burning sensation, swelling, blistering, and necrosis. Exercise caution to avoid local extravasation during intravenous administration of MultiHance.
Cardiac Arrhythmias: Cardiac arrhythmias have been observed in patients receiving MultiHance in clinical trials. Assess patients for underlying conditions or medications that predispose to arrhythmias. The effects on QTc by MultiHance dose, other drugs, and medical conditions were not systematically studied.
Interference with Visualization of Certain Lesions: Certain lesions seen on non-contrast images may not be seen on contrast images. Exercise caution when interpreting contrast MR images in the absence of companion non-contrast MR images.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most commonly reported adverse reactions are nausea (1.3%) and headache (1.2%).
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy: GBCAs cross the human placenta and result in fetal exposure and gadolinium retention. Use only if imaging is essential during pregnancy and cannot be delayed.
Lactation: There is no information on the effects of the drug on the breastfed infant or the effects of the drug on milk production. However, limited literature reports that breastfeeding after MultiHance administration to the mother would result in the infant receiving an oral dose of 0.001%-0.04% of the maternal dose.
Pediatric Use: MultiHance is approved for intravenous use for MRI of the CNS to visualize lesions with abnormal blood brain barrier or abnormal vascularity of the brain, spine, and associated tissues in pediatric patients from birth, including term neonates, to less than 17 years of age. Adverse reactions in pediatric patients were similar to those reported in adults. No dose adjustment according to age is necessary in pediatric patients two years of age and older. For pediatric patients, less than 2 years of age, the recommended dosage range is 0.1 to 0.2 mL/kg. The safety of MultiHance has not been established in preterm neonates.
ProHance (Gadoteridol) Injection, 279.3 mg/mL
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Contraindicated in patients with known allergic or hypersensitivity reactions to ProHance.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Risk Associated with Intrathecal Use: Intrathecal administration of GBCAs can cause serious adverse reactions including death, coma, encephalopathy, and seizures. The safety and effectiveness of ProHance have not been established with intrathecal use and ProHance is not approved for intrathecal use.
Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis: NSF has occurred in patients with impaired elimination of GBCAs. Higher than recommended dosing or repeated dosing appears to increase risk.
Hypersensitivity Reactions: Anaphylactic and anaphylactoid reactions have been reported, involving cardiovascular, respiratory, and/or cutaneous manifestations. Some patients experienced circulatory collapse and died. In most cases, initial symptoms occurred within minutes of administration and resolved with prompt emergency treatment. Prior to ProHance administration, ensure the availability of trained personnel and medications to treat hypersensitivity reactions. Consider these risks, especially in patients with a history of hypersensitivity reactions or a history of asthma or other allergic disorders.
Gadolinium Retention: Gadolinium is retained for months or years in several organs. The highest concentrations have been identified in the bone, followed by brain, skin, kidney, liver, and spleen. Linear GBCAs cause more retention than macrocyclic GBCAs. Consequences of gadolinium retention in the brain have not been established, but they have been established in the skin and other organs in patients with impaired renal function.
Acute Kidney Injury: In patients with chronically reduced renal function, acute kidney injury requiring dialysis has occurred with the use of GBCAs. The risk of acute kidney injury may increase with increasing dose of the contrast agent; administer the lowest dose necessary for adequate imaging.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most commonly reported adverse reactions are nausea and taste perversion with an incidence ≥ 0.9%.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy: GBCAs cross the human placenta and result in fetal exposure and gadolinium retention. Use only if imaging is essential during pregnancy and cannot be delayed.
Lactation: There are no data on the presence in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. However, published lactation data on other GBCAs indicate that 0.01 to 0.04% of the maternal gadolinium dose is present in breast milk.
Pediatric Use: The safety and effectiveness of ProHance have been established for use with MRI to visualize lesions with abnormal blood brain barrier or abnormal vascularity of the brain, spine, and associated tissues in pediatric patients from birth, including term neonates, to 17 years of age. Adverse reactions in pediatric patients were similar to those reported in adults. No case of NSF associated with ProHance or any other GBCA has been identified in pediatric patients ages 6 years and younger.
You are encouraged to report negative side effects of prescription drugs to the FDA. Visit www.fda.gov/medwatch or call 1-800-FDA-1088.
Please click here for full Prescribing Information and Patient Medication Guide for additional safety information for MultiHance (gadobenate dimeglumine) injection, 529 mg/mL.
Please click here for full Prescribing Information and Patient Medication Guide for additional safety information for MultiHance Multipack.
Please click here for full Prescribing Information and Patient Medication Guide for additional safety information for ProHance (Gadoteridol) Injection, 279.3 mg/mL.
Please click here for full Prescribing Information and Patient Medication Guide for additional safety information for ProHance Multipack.
MultiHance is manufactured for Bracco Diagnostics Inc. by BIPSO GmbH – 78224 Singen (Germany) and by Patheon Italia S.p.A, Ferentino, Italy.
ProHance is manufactured for Bracco Diagnostics Inc. by BIPSO GmbH – 78224 Singen (Germany).
MultiHance is a registered trademark of Bracco International B.V.
MultiHance Multipack is a trademark of Bracco International B.V.
ProHance is a registered trademark of Bracco Diagnostics Inc.
ProHance Multipack is a trademark of Bracco Diagnostics Inc.
All other trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Bracco Diagnostics Inc.
259 Prospect Plains Road, Building H
Monroe Township, NJ 08831 USA
Phone: 609-514-2200
Toll-Free: 1-877-272-2269 (U.S. only)
Fax: 609-514-2446
© 2024 Bracco Diagnostics Inc. All Rights Reserved.